

Make all necessary formatting changes in the Modify Style dialog box.
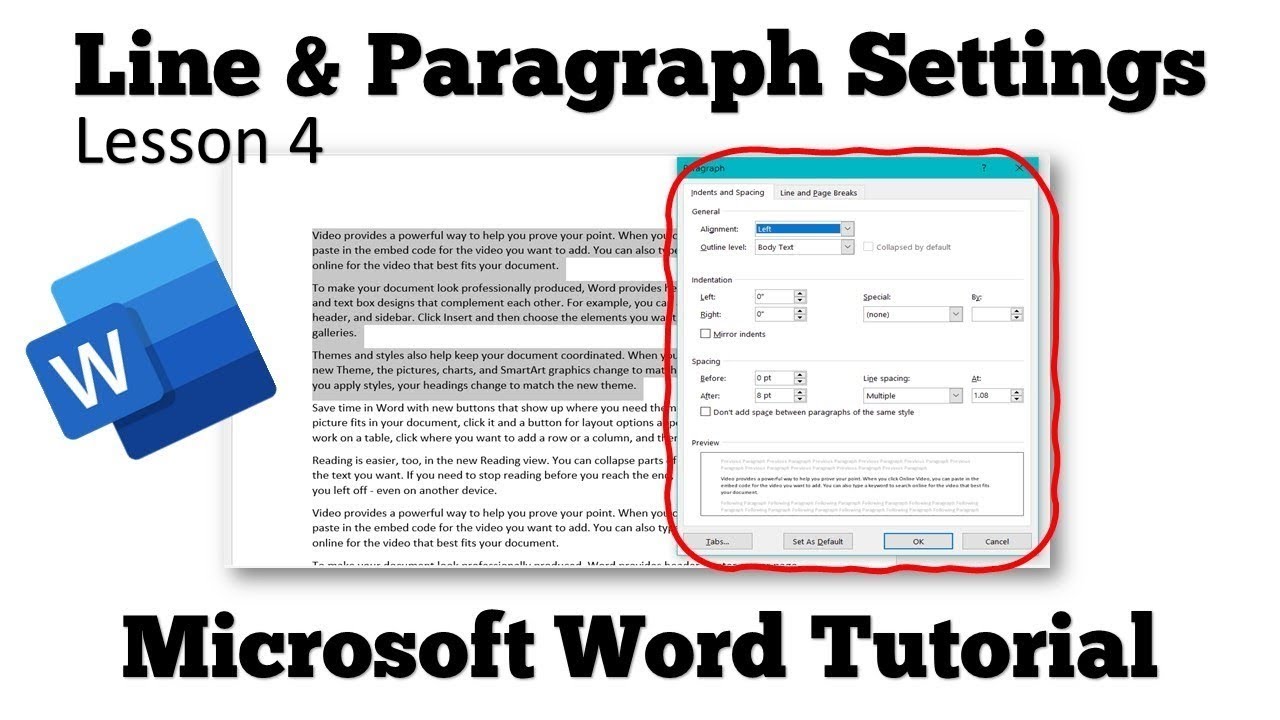
 Right-click (PC) or Control-click the heading level in the Styles group, and then select Modify from the shortcut menu. Select the Home tab in the ribbon (see figure 1). For this tutorial, we’ll stick with the basics: font, font size, emphasis (i.e., bold, italic, or underlined), color, alignment, spacing, and indentation. There are many ways to change styles in Word. The following steps show how to customize the built-in heading styles in an individual Word document. How to Customize Word’s Built-In Heading Styles If you only use a large font size for headings, people who use screen readers will have less information about how your document is organized.* Most importantly, screen reading software can identify your heading hierarchy based on Word’s styles. Create bookmarks in a PDF using Adobe Acrobat. Create an automatic or custom table of contents. For example, Word’s heading styles help you perform the following tasks: However, you won’t have access to several important features if you use a large font size rather than Word’s official heading styles. You can make any text in Word look like a heading by using a large font size.
Right-click (PC) or Control-click the heading level in the Styles group, and then select Modify from the shortcut menu. Select the Home tab in the ribbon (see figure 1). For this tutorial, we’ll stick with the basics: font, font size, emphasis (i.e., bold, italic, or underlined), color, alignment, spacing, and indentation. There are many ways to change styles in Word. The following steps show how to customize the built-in heading styles in an individual Word document. How to Customize Word’s Built-In Heading Styles If you only use a large font size for headings, people who use screen readers will have less information about how your document is organized.* Most importantly, screen reading software can identify your heading hierarchy based on Word’s styles. Create bookmarks in a PDF using Adobe Acrobat. Create an automatic or custom table of contents. For example, Word’s heading styles help you perform the following tasks: However, you won’t have access to several important features if you use a large font size rather than Word’s official heading styles. You can make any text in Word look like a heading by using a large font size.  How to Customize Word’s Built-In Heading Stylesīefore jumping to the tutorial, let’s discuss the importance of using Word’s heading styles. How to Create Headings Using Word’s Built-In Heading Styles. Or, do you want to add numbers to your headings? Check out “ How to Add and Modify Heading Numbers in Microsoft Word (PC & Mac).” Do you want to create your own custom heading styles separate from Word’s built-in styles? Check out “ How to Create a Custom Heading Style in Microsoft Word” and “ How to Create a Custom Heading Style in Microsoft Word for Mac.”
How to Customize Word’s Built-In Heading Stylesīefore jumping to the tutorial, let’s discuss the importance of using Word’s heading styles. How to Create Headings Using Word’s Built-In Heading Styles. Or, do you want to add numbers to your headings? Check out “ How to Add and Modify Heading Numbers in Microsoft Word (PC & Mac).” Do you want to create your own custom heading styles separate from Word’s built-in styles? Check out “ How to Create a Custom Heading Style in Microsoft Word” and “ How to Create a Custom Heading Style in Microsoft Word for Mac.”












